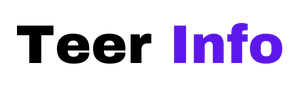In the digital age, where our lives are intricately intertwined with technology, maintaining a smoothly running computer system is essential. Imagine this: you sit down to work or indulge in your favorite game, only to be met with sluggish performance and eerie lags. The culprit? The notorious Antimalware Service Executable (MsMpEng.exe), a vital component of Windows Defender that sometimes goes rogue, consuming an alarming amount of memory. This frustrating scenario can leave users scratching their heads—how can software designed to protect us become the very source of our tech woes?
Fear not! In this article, we’ll delve into the reasons behind this high memory usage and equip you with practical solutions to reclaim your computer’s speed and efficiency. From adjusting settings within Windows Defender to exploring alternative security options, we’ll guide you step-by-step through troubleshooting techniques that ensure your device runs like a well-oiled machine once more. Whether you’re a seasoned tech enthusiast or just someone who wants their PC back in fighting shape, our insights will help demystify this common issue and empower you to take control of your computing experience.
What is Antimalware Service Executable?
Antimalware Service Executable is a core component of Microsoft Defender, the built-in antivirus solution for Windows. It operates in the background, scanning files and processes to protect your system from malicious threats. While it is essential for maintaining security and preventing malware infections, some users encounter an issue where this service consumes an excessive amount of memory. This can lead to performance slowdowns, making tasks cumbersome and disrupting productivity.
One interesting aspect of Antimalware Service Executable is its dual role: not only does it guard against threats in real-time, but it also conducts periodic scans that evaluate the entire system for vulnerabilities. However, this aggressive approach can sometimes overload system resources—especially on machines with limited hardware capabilities or when multiple applications are running simultaneously. Understanding how and when these scans occur can empower users to optimize their experience; for instance, adjusting active hours or scheduling scans during off-peak times can alleviate high memory usage while still ensuring robust protection against malware. Balancing security with performance is crucial in the digital age where efficiency matters just as much as safety.
Causes of High Memory Usage
High memory usage can stem from a variety of underlying causes that often go unnoticed. One significant factor is the sheer volume of files and processes running simultaneously on your system. As the Antimalware Service Executable operates in real-time to scan files, it can inadvertently compete for resources with other applications. This becomes particularly pronounced in systems with limited RAM or when overloaded with demanding tasks, leaving less room for essential operations.
Another contributing element could be outdated software or drivers that fail to interface efficiently with the Antimalware Service Executable. Software incompatibility not only hinders performance but also leads to redundant memory allocation as programs attempt to execute processes multiple times. Additionally, certain malware strains have evolved to masquerade as legitimate processes, tricking your security software into overworking itself while compromising overall system efficiency. By understanding these diverse causes, users can take proactive steps—such as optimizing their system configurations and ensuring updates are applied—to mitigate high memory usage and improve overall performance.
Signs You’re Experiencing High Memory Usage
High memory usage can manifest in various ways, and being alert to these signs is crucial for maintaining system performance. One primary indicator is the noticeable slowdown of your device, with tasks that once ran seamlessly becoming sluggish or unresponsive. You might also experience frequent stuttering during video playback or when using graphic-intensive applications, which can be frustrating if you’re in the midst of important work or enjoying leisure activities.
Another telltale sign involves increased load times for programs and applications. Opening files or launching software may take significantly longer than usual, often leading you to wonder if something has gone awry. Additionally, unexpected crashes or freezes during routine operations might signal that your memory resources are being stretched too thin. If you’ve noticed multiple background processes consuming substantial RAM without apparent reason, it’s a clear indication that high memory usage may be at play—especially with tools like Antimalware Service Executable potentially hogging resources while running scans or updates. By recognizing these symptoms early on, you can take proactive steps to troubleshoot and restore balance to your system’s performance.

How to Check Resource Utilization
To effectively check resource utilization on your system and address the high memory usage associated with the Antimalware Service Executable, start by leveraging built-in tools like Task Manager and Resource Monitor. Task Manager provides a straightforward interface to view running processes and their respective memory consumption, helping you identify if Microsoft’s Windows Defender is unduly hogging resources during scans or updates. Simply right-click the taskbar, select “Task Manager,” and navigate to the Processes tab for a granular look at memory usage.
For deeper insights, harness Resource Monitor, which can be accessed through Task Manager by clicking on “Performance” and then selecting “Open Resource Monitor.” This tool enables you to drill down into disk activity, network utilization, and CPU usage specific to Windows Defender or any other services that may be conflicting. By observing patterns in resource spikes—particularly during scheduled scans—you can adjust settings within Windows Security to mitigate impacts on your system’s performance. Moreover, consider temporarily disabling real-time protection when conducting heavy tasks—that balances security with efficiency without compromising your overall safety online.
Methods to Fix High Memory Usage
One effective method to mitigate high memory usage caused by the Antimalware Service Executable is to schedule Windows Defender scans during off-peak hours. By configuring automated scans when you’re less likely to be using your computer, you can significantly reduce the strain on system resources during busy times. This not only helps improve performance but also maintains robust protection against threats without constant interruptions.
Another approach involves adjusting the ‘Real-time Protection’ settings. While it’s crucial for safeguarding your device, you may choose to temper its intensity. Temporarily disabling this feature while executing specific tasks, such as gaming or graphic design work, can result in noticeable performance improvements. Don’t forget that opting for a third-party antivirus solution could further alleviate pressure on system resources; just ensure that it complements Windows security rather than conflict with it for optimal results.
Lastly, regularly updating your operating system and antivirus definitions can streamline memory use by optimizing how these processes run in the background. Keeping software up-to-date not only introduces enhancements and fixes bugs but often improves overall efficiency—lessening the impact of services like Antimalware Service Executable on your system’s RAM. Consider pairing this practice with disk cleanup sessions to eliminate unnecessary files cluttering memory paths, making way for smoother operations across programs and applications alike.
Adjusting Windows Defender Settings
Adjusting Windows Defender settings can significantly alleviate the high memory usage caused by the Antimalware Service Executable. One effective approach is to fine-tune your scan schedules and exclusions. By setting scans to occur during off-peak hours—when you’re less likely to be using your computer—you ensure that system resources are not monopolized, allowing for smoother day-to-day operations. Additionally, consider excluding certain folders or file types from real-time scanning; this could include virtual machine files or large media libraries that don’t pose threats but strain memory usage.
Furthermore, take a closer look at Defender’s behavior monitoring options. Disabling some of these features may not drastically affect security but can free up valuable system resources—especially if you frequently run applications that demand high processing power, like video editing software or gaming platforms. Always balance security with performance; updating definitions twice a week instead of daily can still keep your device safe while minimizing resource strain. These adjustments empower you to customize Windows Defender based on your unique needs, striking an optimal balance between protection and performance.
Conclusion: Managing Antimalware Service Effectively
In conclusion, managing the Antimalware Service Executable effectively is key to maintaining a balance between robust system protection and optimal performance. Understanding its role within Windows Defender is essential; it acts as a guardian against digital threats while also consuming system resources during scans and updates. By strategically scheduling scans during off-peak hours, users can mitigate high memory usage without sacrificing security.
Moreover, tuning your antimalware settings—such as adjusting real-time protection or excluding specific files that you know are safe—can further enhance performance. Regularly updating both the operating system and antimalware definitions ensures that your defenses remain resilient against emerging threats, which in turn minimizes the need for intensive resource consumption during alert periods. Ultimately, fostering an environment where you manage system resources mindfully will lead to a smoother experience without compromising on safety.